Most Common Cannabinoids
Among the more then one hundred cannabinoids identified in Cannabis Sativa L., majority can be categorized as analogs of tetrahydrocannabidiol (Δ9 -THC) or cannabidiol (CBD).
Among the more then one hundred cannabinoids identified in Cannabis Sativa L., majority can be categorized as analogs of tetrahydrocannabidiol (Δ9 -THC) or cannabidiol (CBD).
Research on CBD, and the Cannabis Sativa L. plant altogether, has progressed slowly, partly due to the enduring stigma associated with the plant. Despite these challenges, investigations into its bioactivity and potential as a therapeutic aid have adanced. Over the past two decades, both scientific research and anectodal evidence suggest that CBD holds promise as a valuable ally in the treatment and management of various health conditions.
Unlike Δ9-THC, CBD does not induce psychoactive effects. Instead, its interactions with the andocannabinoid system point towards theurapeutic benefits, including pain relief, anti-anxiety properties, and anti-inflamatory effects.
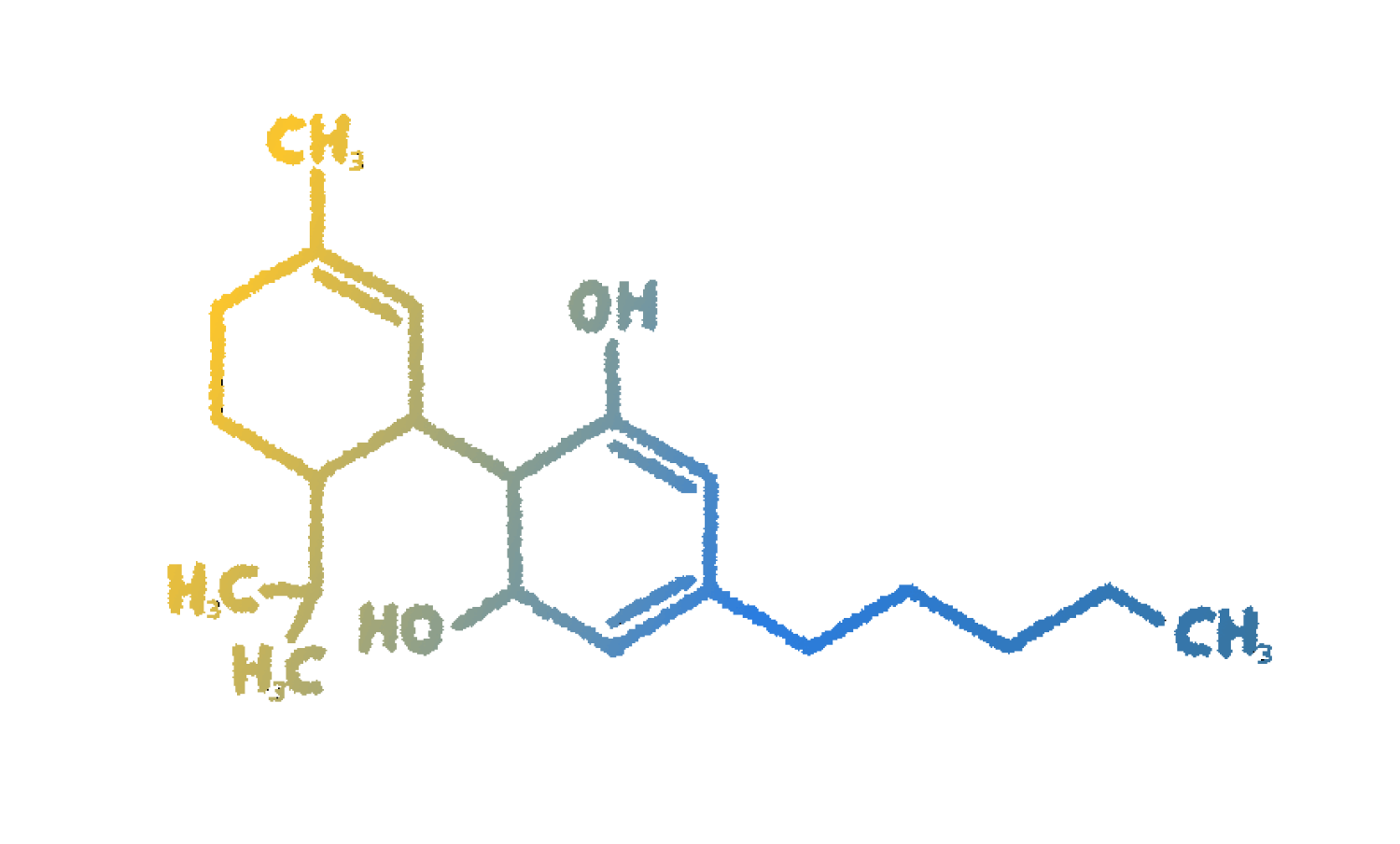
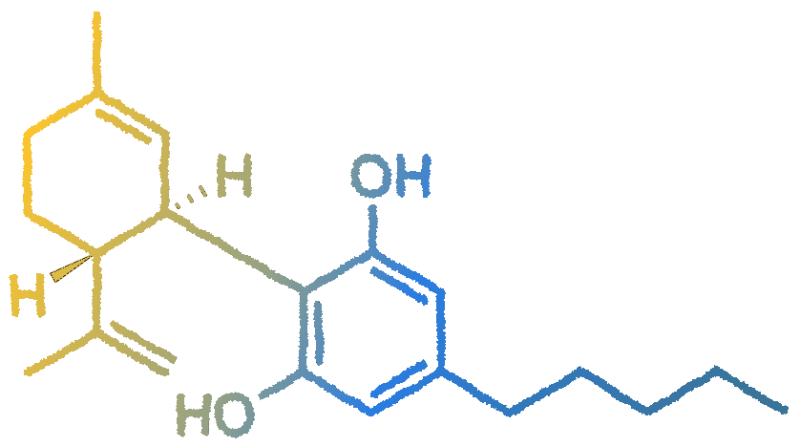
When decarboxylation occurs after heat or sunlight exposure of the plant, CBDA converts to CBD. In other words, CBDA is the raw form or predecessor to CBD.
CBDA interacts with the endocannabinoid system by inhibiting enzymes associated with inflammation after an injury or infection – by blocking them, CBDA can relieve inflammation and inflammation associated pain and, apart from that, it has been found tha CBDA affects levels of serotonin, a chemical that is vital to core human functions like motor skills, sleeping, eating, digestion, and emotions.
Δ9-THC stands out as the primary psychoactive phytocannabinoid, boasting a diverse range of pharmacological properties.
Renowned for its psychological effects and commonly utilized for recreational purposes, THC demonstrates the highest potency at both CB1 and CB2 receptors among all phytocannabinoids. This suggests that, beyond its well-known psychological impacts, THC also exerts significant physiological effects.
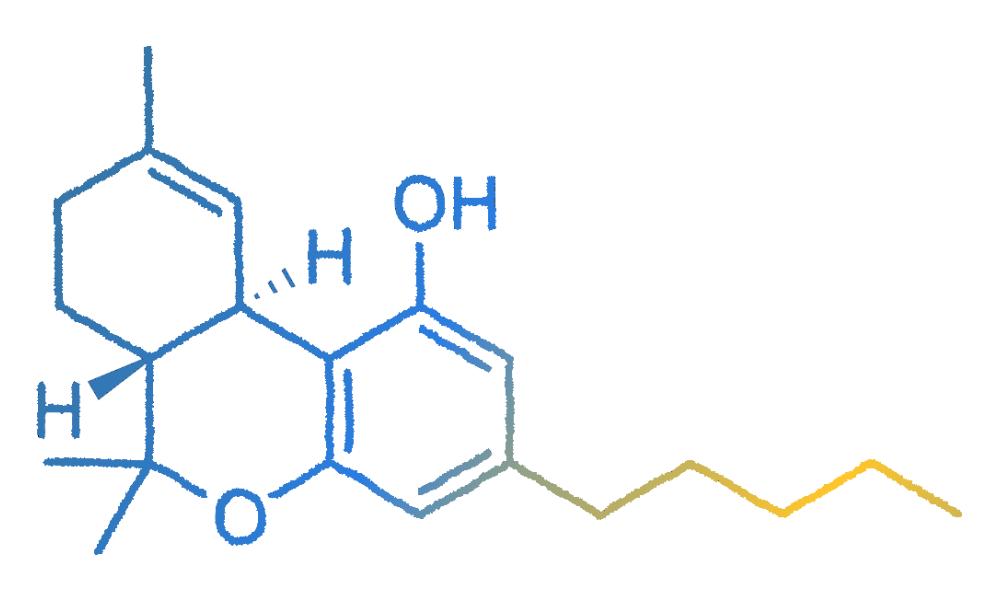
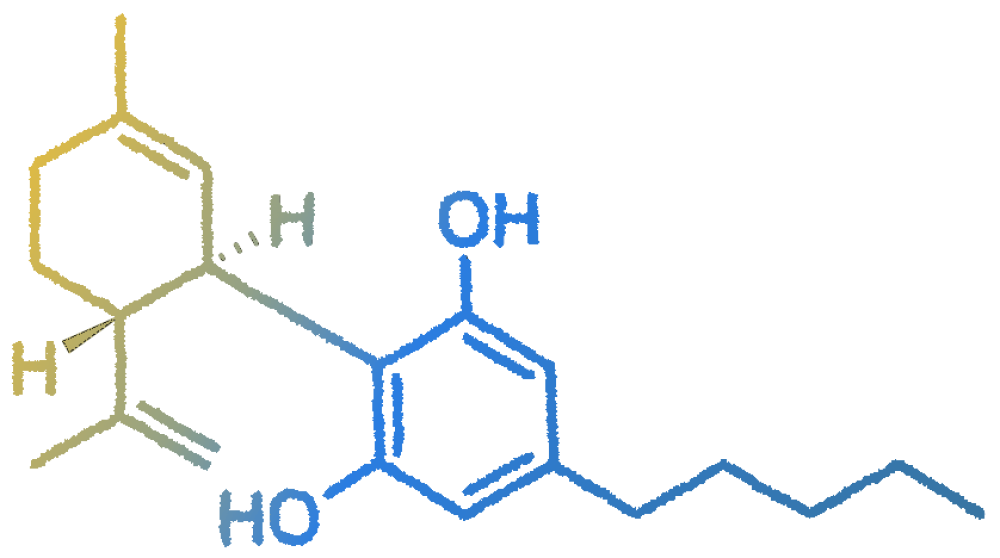
CBN was the first phytocannabinoid to be isolated in a pure form, arising from the natural process occurring when Δ9-THC, even in optimal storage conditions, undergoes exposure to UV light and/or heat over time.
When paired with CBD, individuals frequently explore CBN products for their potential to promote sleep and relaxation. From a scientific standpoint, CBN has been recognized for its potential as an analgesic and anti-inflammatory agent. Additionally, it has demonstrated efficacy against various antibiotic-resistant bacteria and serves as a non-intoxicating alternative appetite stimulant.
CBC stands out as one of the most prevalent minor cannabinoids present in cannabis and is characterized by its non-intoxicating nature.
Similar to CBN, CBC exhibits potent antibiotic properties, proving effective against infections resistant to alternative treatments. Cannabichromene has been linked to addressing and preventing acne, displaying a positive impact on neural stem progenitor cells crucial to healthy brain function. In the context of cancer treatment, it demonstrates potential in suppressing both inflammation and tumor growth.
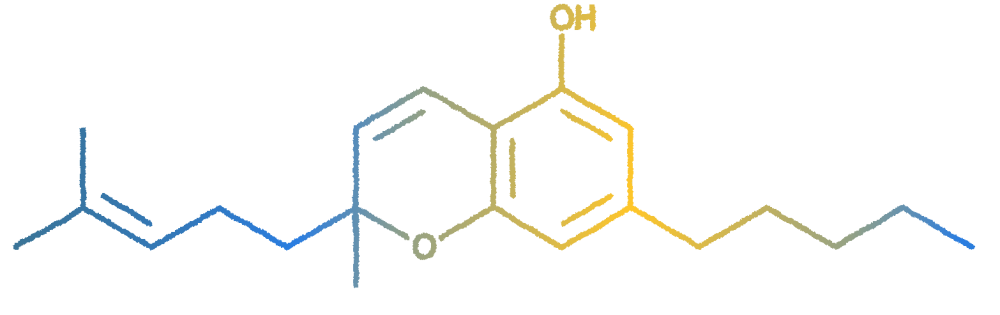
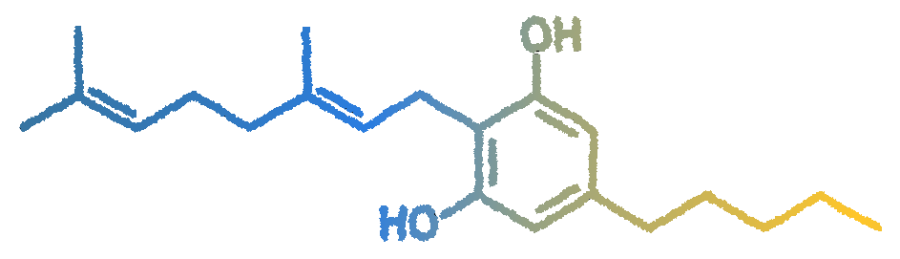
CBG serves as the primary precursor of phytocannabinoids. All major cannabinoids originate from CBGA – CBG in its acid form, earning it the moniker “mother of all cannabinoids.”
Preliminary research suggests CBG may have potential applications for various concerns. CBG exhibits effectiveness as a pain reliever and anti-inflammatory agent and, aditionally, it functions as an antibacterial agent, offers assistance with psoriasis and other skin conditions, and may play a role in emotional regulation similar to an antidepressant.
Sign up for the newsletter and get a 10% discount on your first purchase.
Accepted payments: Visa, MasterCard, Maestro, Amex and more.

© ØYL • Tous droits réservés. • oyl-cbd.com
Design by Bureau Carné